Last summer we looked at the impact that the rise in coffee and cocoa prices was having on margin requirements. At the time we saw a 25% increase in the Initial Margin rate for cocoa based on a steady increase in prices. For coffee it was a different picture, with margins falling and becoming a lower percentage of value based on a drop in volatility.
Since then, however, there has been a significant increase in the price of both commodities.
A prolonged heatwave in Vietnam and a late start to the rainy season are contributing to damage to crops of robusta coffee beans, used in instant coffee. This has been compounded by supply issues, including the Houthi attacks on shipping in the gulf area.
There have also been weather issues in Brazil, with heavy rain damaging the crops of the more expensive arabica coffee. Buyers are also building reserves of the beans ahead of a new EU regulation that comes into effect in December. After this date suppliers will need to prove that their coffee has not been grown on deforested land.
As a result of these issues, there has been a significant increase in global coffee prices for both robusta and arabica. London robusta future prices have hit a record high whilst arabica futures have risen to their highest level since September 2022.
Meanwhile, cocoa is facing a similar crisis. A combination of old trees, crop disease and bad weather have led to crop shortages and the closure of production plants. This lack of supply is then having an impact on prices.
Cocoa future prices have increased about 70% since the beginning of March to reach record levels. Prices are expected to remain volatile in the near future.
So what has been the impact on margin requirements?
Coffee Margin Requirements
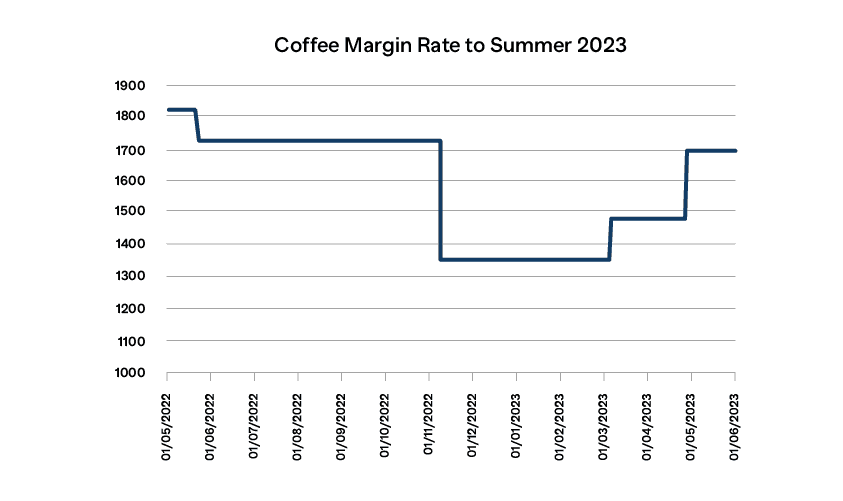
Between Summer 2022 and Summer 2023 coffee margins moved around based on changes in prices and volatility. By the end of the period they ended slightly down, and at a lower percentage of value, as can be seen in the chart below:
If we now extend this chart to include changes to date we can see that there has been a significant increase in requirements of over 50%.
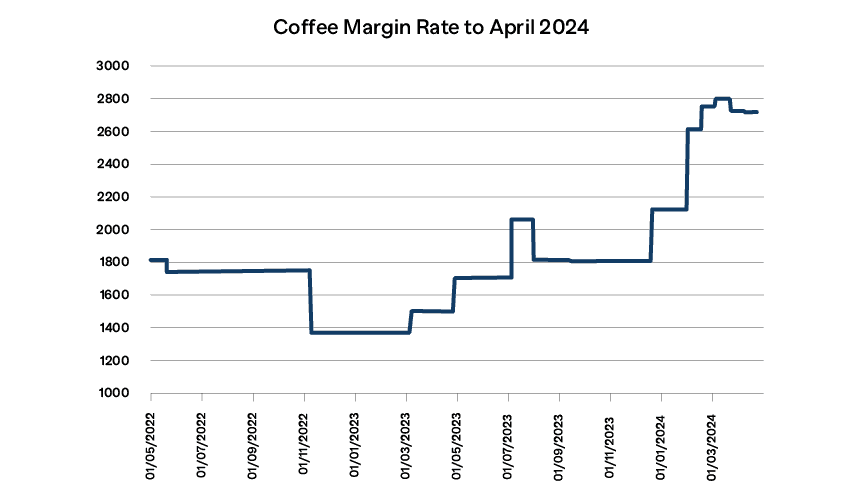
However, the rise in Initial Margin is not as bad as it could have been. In the same period the price has increased by over 60%, so as a percentage of value the requirements have actually fallen, reflecting the steady rather than sudden increase in prices and therefore relatively low volatility.
Cocoa Margin Requirements
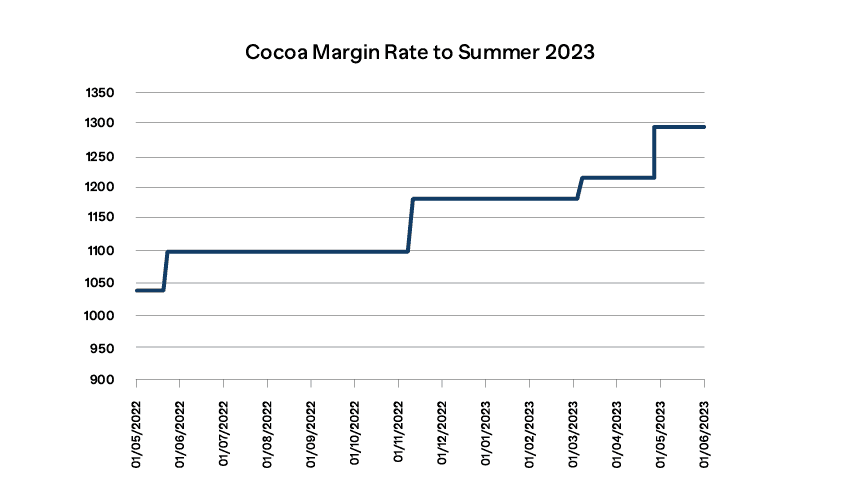
Summer 2022 to Summer 2023 showed a steady increase in cocoa prices matched by a similar increase in margins of about 25%:
If we extend this chart to April 2024 we can see that this trend of increasing Initial Margin has continued but at a much increased pace:
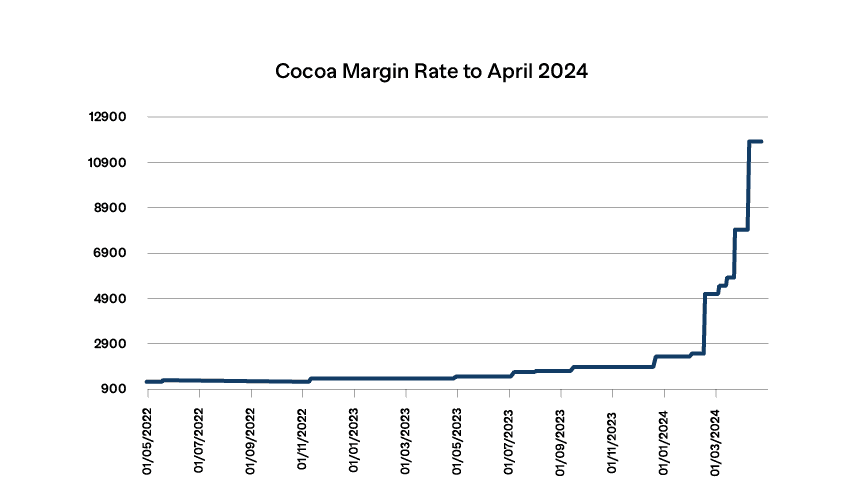
Cocoa margin requirements are now around 8 times the level that they were last Summer. In the same period cocoa prices have risen to less than 4 times the level seen in the middle of last year. This means that cocoa Initial Margin is now a significantly greater proportion of value than previously, reflecting the level of volatility in the market.
Conclusion
The margin requirements for both coffee and cocoa have risen significantly on the back of price rises caused by a combination of weather and geopolitical related issues. However, the impact this has had on the margin requirements has not been consistent across both products.
The price rises for coffee have been relatively steady resulting in more stable Initial Margin, with the increases leveling off, and more recently even seeing a small reduction in requirements.
Cocoa prices, on the other hand, have been more volatile and this has resulted in a rapid increase in Initial Margin since the start of the year. The last two rises alone have been around 50%, with requirements more than doubling since the beginning of March.
These two contracts show just how much margin can change in a world dominated by climate change and geopolitical instability. And the same is true for many other agricultural products. Firms need to take into account the effect of price changes on Initial Margin and how this can impact their liquidity requirements when making trading and funding decisions.